Vitamin D is good for acid reflux. It aids digestion and has a role in preventing acid reflux symptoms, but it’s not a “magic pill” that’s going to cure your heartburn by itself. Rather, making sure you have enough vitamin D will help you manage gastrointestinal problems, along with improving your overall health. But how do I make sure I get enough vitamin D? And what are the best sources of vitamin D for me?
What is heartburn?
Heartburn, also called acid reflux, is the painful burning sensation you feel in your chest when acidic contents of the stomach gets past your lower esophageal sphincter muscle and moves back up into your esophagus or food pipe.
The job of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is to shut tight so hydrochloric acid in your stomach and food can’t back up into your esophagus.
If you have acid reflux, either your LES doesn’t close properly or there is too much pressure on your stomach.
Food and some medications, including counter medications can cause your sphincter muscle to relax and allow food to reflux.
Too much pressure on your stomach typically happens when you eat large meals or wear tight clothes or belts around your stomach, which can force your sphincter muscle open and reflux occurs.
Regular acid reflux causes inflammation of the esophagus. If left untreated, heartburn can evolve into gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). You will also be at increased risk of developing peptic ulcers, Barrett’s Esophagus and esophageal cancer in extreme cases.
Common heartburn and GERD symptoms
Depending on the severity of your heartburn or, your side effects may vary. A person’s symptoms of GERD include:
- chest pain or stomach pain
- burning sensation in your chest
- bitter taste in your mouth
- sore throat
- difficulty swallowing
- feeling like you have something stuck in your throat
- coughing or hoarseness
Causes of heartburn
- large meals
- spicy foods
- fried and fatty foods, including high fat dairy products
- acidic foods
- carbonated drinks including sodas and ginger ales
- chronic stress
- too much or not enough stomach acid production
- excess alcohol
- obesity
- alcohol
- smoking
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin. This means that vitamin D is found in some foods that contain fat, and is stored in your body’s fat cells. Your body can also make it’s own vitamin D when your skin is exposed to the sun.
Many people can get enough vitamin D by exposing their skin to the sun for a short time everyday. This is easy if you live in a hot climate.
If this doesn’t apply to you, you will probably need to get your vitamin D from food or take a dietary supplement.
Sun exposure through car windscreens and sunscreen will prevent your body from making it’s own vitamin D from the sun.
The main role of vitamin D is to help your body absorb other nutrients. Low vitamin D levels mean your body isn’t getting all the nutrition it could from the foods you eat. And this can effect your health in lots of ways, not just digestion and heartburn problems.
Vitamin D also supports your immune system by fighting infection and controlling inflammation in your gut.
Vitamin D2 vs Vitamin D3
There are 2 types of vitamin D:
Vitamin D2 is made from plants and is found in foods that have vitamin D added to them (these are called fortified foods) and some dietary supplements. So if you’re vegan and wanting to take vitamin supplements, you should look for vitamin D2.
Vitamin D3 is naturally produced in the human body and is found in animal foods. It is thought that Vitamin D3 give s best results by helping your body absorb nutrients better than vitamin D2.
Is vitamin D good for acid reflux?
Vitamin D definitely has a role to play in digestion, and a new study suggests vitamin D may play a bigger role in your aiding digestion than what is currently known. Below are the ways in which vitamin D can help heartburn and indigestion.
Vitamin D and absorption of nutrients
There is a lot of research showing a link between low vitamin D levels and low levels of calcium and magnesium. With low vitamin D levels, your body cannot absorb all the calcium it should from the food you eat.
Over time, a vitamin D deficiency could lead to increased risk of bone fractures in older adults, Alzheimer dementia and overall mortality.
Without enough vitamin D the muscles in your digestive system may not work as they should.
Calcium and magnesium both have and important role to play in digestion and proper functioning of your gastrointestinal tract.
These nutrients help your muscles relax and contract and help our digestive system work properly.
Your whole gastrointestinal tract contains muscles which are responsible for peristalsis, which is a wave like muscle movement that keeps moving food along.
In addition, your lower esophageal sphincter muscle stops food from refluxing back into your esophagus or food pipe.
Also, your pyloric sphincter, the muscle band between your stomach and small intestines, needs to be working properly too. If food is not transferred to your small intestines when it should, food will start fermenting in your stomach and this will cause gas to build up, put pressure on your sphincter muscle and acid reflux can occur.
Vitamin D and infection control
Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory properties and antimicrobial properties that helps your immune system prevent infections and inflammation in your gut.
One of the main causes of heartburn is said to be infection in your gastrointestinal system. These infections hinder digestion, inhibit hydrochloric acid production and digestive enzymes in your stomach, which lead to acid reflux and heartburn.
When you have enough vitamin D, your body can make special compounds that have antimicrobial qualities which fight infection and keep inflammation at bay.
If you have a vitamin D deficiency, your gastrointestinal tract doesn’t function properly. Your digestive muscles don’t work as they should to keep food moving through your digestive system and to prevent reflux. And your immune system’s ability to prevent infection and inflammation is hampered. These factors may set off a chain reaction that causes heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
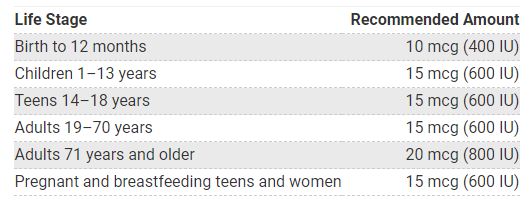
How much vitamin D do you need?
The amount of vitamin D you need each day depends on your age. Average daily recommended amounts are listed below in micrograms (mcg) and International Units (IU):
Vitamin D deficiency
If you think you might have low levels of vitamin D, seeking professional medical advice is the best way forward. There are some simple tests that can be done to check for vitamin deficiencies.
It may take several years to correct a vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin Supplements
Given that vitamin D deficiency often goes hand in hand with calcium and magnesium deficiencies, if you’re going to consider vitamin supplements, you may want to choose a multivitamin that contains these three nutrients. Your health care provider is best placed to offer you advice on this.

10 ways to get more vitamin D and help avoid heartburn
I’ve broken this up into two parts:
- Non-dietary sources of vitamin D (ie. not food)
- Dietary sources of vitamin D
Non-dietary sources of vitamin D
1. Sun
Your body makes its own vitamin D when skin is exposed to sun. Generally, the amount of vitamin D you can get from the sun depends on how close you are to the equator, and what month it is. You can view this chart for a rough guide of how much sun exposure you need to get enough vitamin D from the sun.
Why not combine getting vitamin D from the sun with other beneficial remedies for heartburn such as gentle, low impact exercise or meditation?
Remember that sun exposure through sunscreen and car windows will hamper vitamin D absorption a lot. So you need to consider the consequences of not protecting your skin from the sun vs the need for skin exposure to vitamin D. Generally speaking, if you live in a hot climate, 20 minutes of gentle morning sun may give you enough vitamin D for the day. There are other ways to get enough vitamin D if you are concerned about sun exposure.
2. Vitamin D supplements
Vitamin D supplements are readily available and do their job really well. Given the role vitamin D has in nutrient absorption, rather than just taking a vitamin D supplement, consider taking a multivitamin that also contains calcium and magnesium, as it is likely you may be deficient in these nutrients as well.
Make sure you do your research and get good quality vitamins that are in a form that is readily absorbed by your body. Your health care provider can help you with this.
Dietary sources of vitamin D
3. Fresh oily fish

Fresh oily fish like salmon, sardines, perch, and rainbow trout contain quite a bit of Vitamin D (about 150 units per ounce). Plus, you also get omega 3 fatty acids which keeps your heart healthy.
4. Canned fish
Canned fish, especially tuna, is another good source of vitamin D. Light tuna that comes in cans is your best option. It contains 150 units in every 4 ounce serving, whereas canned sardines contain a mere 40 units for every pair of fish.
5. Dole’s Portobello mushrooms
You can also try Dole’s Portobello Mushrooms, which are exposed to UV light. Mushrooms are like human skin in that they produce Vitamin D in the presence of ultraviolet rays and store it. And since most other mushrooms are grown in the dark, if you are after Vitamin D, then this variety is the one to go for. They contain 400 units per 3 ounces.
6. Milk and yogurt
Milk or yogurt can also be your source of vitamin D, but remember, while milk and yogurt provide instant relief, these products can give you heartburn after a while. Find out which milk is best for your acid reflux, keeping in mind that other milks and milt alternative will not contain the same amounts of vitamin D as dairy products.
Natural cow’s milk gives you 100 units per 8 ounce glass, and yogurt will give you 80 units of vitamin D in every 6 ounce serve.
7. Products that are fortified with vitamin D
Some orange juices, soy milks and cereals are fortified with vitamin D. But check the labels first to make sure you’ve got the right ones, and check to make sure you’re getting a good amount of vitamin D.
8. Egg yolks
Egg yolks also contain Vitamin D. There are about 40 units in every yolk. But since there is also 200 mg of cholesterol, if you have cardiovascular disease, you should ideally go for another source of Vitamin D.
9. Beef liver
A less appealing option for some is beef liver. From beef liver you get about 50 units from every 3.5 ounce serving. Like eggs, beef liver is high in cholesterol and is best avoided if you have cardiovascular disease.
10. Cod liver oil
Since oily fish has already been mentioned, cod liver oil shouldn’t come as a surprise! And in fact, one tablespoon of this stuff contains a whopping 1,300 units of Vitamin D, so just half that amount (2 teaspoons) takes care of your daily vitamin D requirement.
Other natural remedies for reflux and heartburn
There are many natural heartburn remedies you can try to reduce heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease:
- avoid your acid reflux trigger foods
- eat alkaline foods
- eat 4-5 small meals per day
- try probiotics
- allow 2-3 hours after eating/drinking before you lie down
- elevate your head and torso when sleeping
- do exercises that don’t aggravate your heartburn most days
- meditate, since stress can cause acid reflux
- avoid alcohol, or drink moderate amounts of alcohol that are less likely to cause reflux
- quit smoking
FAQs about vitamin D and acid reflux
Does Vitamin D help with stomach problems?
Vitamin D can help you with stomach problems. Without enough vitamin D, the muscles in your digestive system may not work as they should to break down food. And, vitamin D helps your immune system with anti-inflammatory properties and antimicrobial properties that prevent infections and inflammation in your gut.
Can low vitamin D cause reflux?
Acid reflux is often associated with low levels of vitamin D. The main role of vitamin D is to help your body absorb other nutrients. Low vitamin D levels mean your body isn’t getting all the nutrition it could from the foods you eat. And this can effect your health in lots of ways, not just digestion and heartburn problems.
Is Vitamin D Good For Acid Reflux?
Vitamin D is good for acid reflux. If you are eating healthily and getting enough vitamin D, your body is likely to be absorbing all the nutrition it can from food, then that will keep your digestive system working properly. But you can’t rely on vitamin D solely as your acid reflux cure.
You need to make sure you’re getting enough vitamin D, and in conjunction with other natural heartburn remedies, you should see improvement. If your heartburn persists, Seek professional medical advice.
There are many options for getting enough vitamin D, so it should hardly be a problem including them in your diet. And as for the good old solution – sunlight, just make sure you take a walk early in the morning when the sun is out but not at its harshest. Not only will you be getting Vitamin D, you will also be exercising, which is an important lifestyle factor in keeping heartburn at bay.
